Bi-metal Sliding Bearing Bushing Design Notes
Lubrication mechanism
When lubrication film exists between two relatively moving surfaces, fiction conditions of the two contact surfaces can be classified in three steps as below:
- Hydrodynamic lubrication
- Boundary lubrication
- Solid lubrication
- Hydrodynamic lubrication
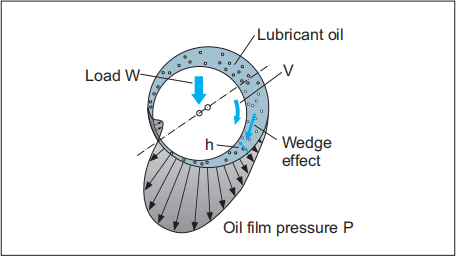
Lubrication film between the two contact surfaces is thick enough and
two contact surfaces are separated completely by viscous oil film. At this time,
frictional force of two contact surfaces are determined by viscous resistance of
lubricant and it take on a very small value (coefficients of friction can be
0.0001^0.01). Under this condition, when shaft is rotated, the oil around the
shaft also rotates due to the viscosity of the lubricant oil and generates oil
pressure at the load area. This phenomenon is called “wedge effect”. The oil
pressure P generated within lubricating oil film is affected by change of
temperature and viscosity of lubricating oil, surface roughness, clearance and
rotational speed of the shaft.
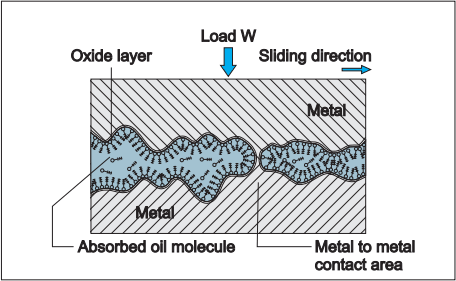
Boundary lubrication
Lubricating oil film between the two
contact surfaces is extremely thin with no viscous hydrodynamic
oil film existing between the two contact surfaces, only a thin
film of absorbed oil molecules exists. Absorptive oil film is
arranged oil molecules that are adhered onto the solid surfaces
and its shear resistance is greater than hydrodynamic oil film.
Frictional force in this area is greater compared to
hydrodynamic lubrication. In the friction contact points, oil
film is frequently broken down. The lubrication condition that
generates a frictional condition such as this is called
'boundary lubrication", in order to decrease the friction under
this condition, selection of self-lubricating bearing may be
desirable.
Solid lubrication (Dry friction)
Under this operating condition, the
two solid surfaces contact directly with each other, there is no
lubricating film such as hydrodynamic film or absorptive oil
film. The frictional force is proportional only to the vertical
load applied to the contact surface of the solid body,
coefficient of friction is independent of the sliding velocity
and the static friction is greater than kinetic friction. Thus,
the self-lubricating bearing material selection is critical to
performance.
Influences on the service life:
Wear and service life of the CSB slide bearings are dependent on the following:
- Specific bearing load
- Sliding speed
- PV value
- Roughness depth of the mating surface
- Mating surface material and Temperature etc.
PV value
The PV value has a considerable influence on the bearing service life. It is
the product of the specific load P and the sliding speed V and the PV is one of
the most important design data, it is recommended a PV value lower than the required
specification will leads to a longer service life.
PV value listed in this catalogues is allowable PV value for radial journal rotational
operation. In many cases, engineers need to take into account the actual bearing
work situation, designing small PV values as far as possible so as to extend the
service life of bearing, of course the suitable data will need a lot of experiments
to verify.
Also, the environmental temperature is necessary to consideration, the clearance
can be changed caused by the dimensional change of the bearing and housing, the
mating material hardness change from the environment temperature, the interference
and so on.
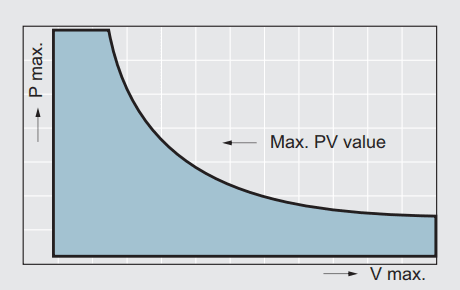
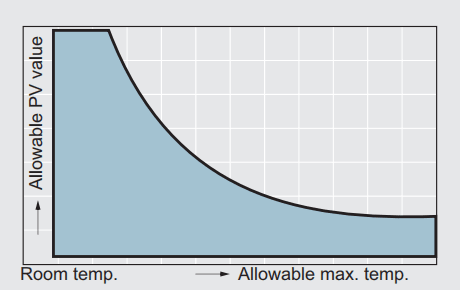
Direction of motion and PV value
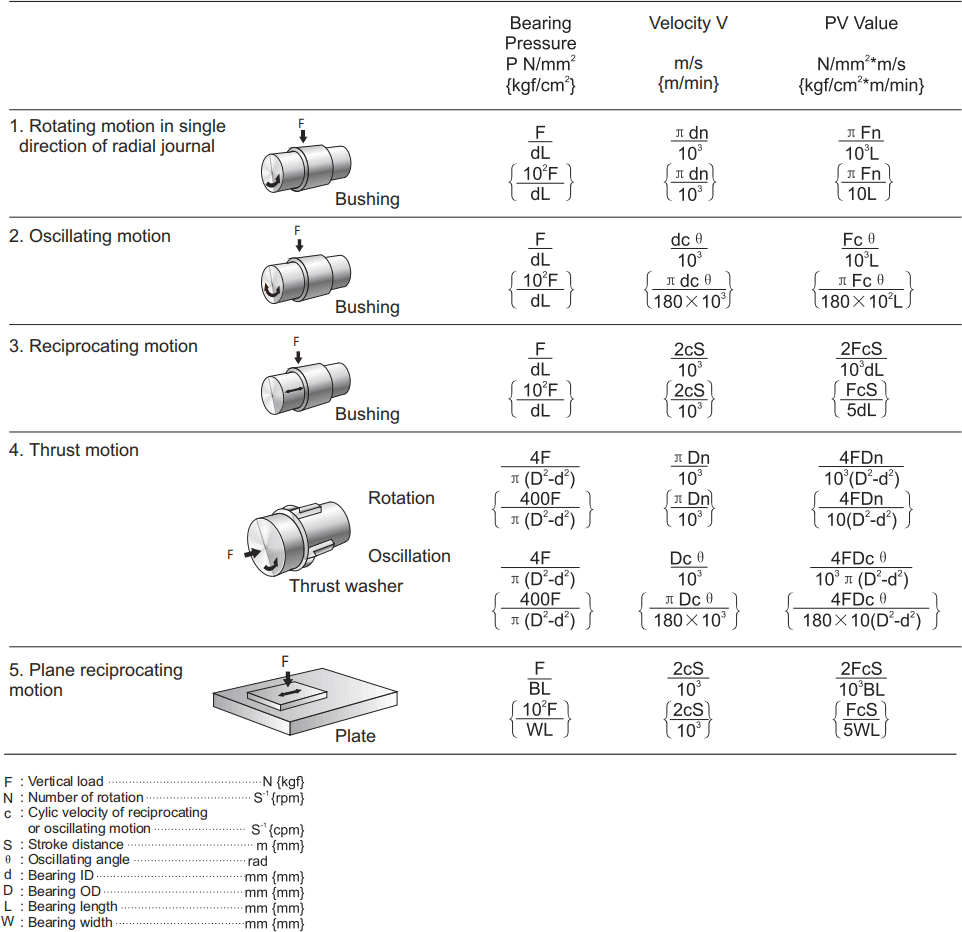
Bearing load
In general, the bearing pressure is obtained by dividing the max. load imposed on the bearing by the pressure supporting area of the bearing. The pressure supporting area is defined as the projected loading area which contacts with the shaft, projected in the direction of the load in cases of a cylindrical and spherical bearings.
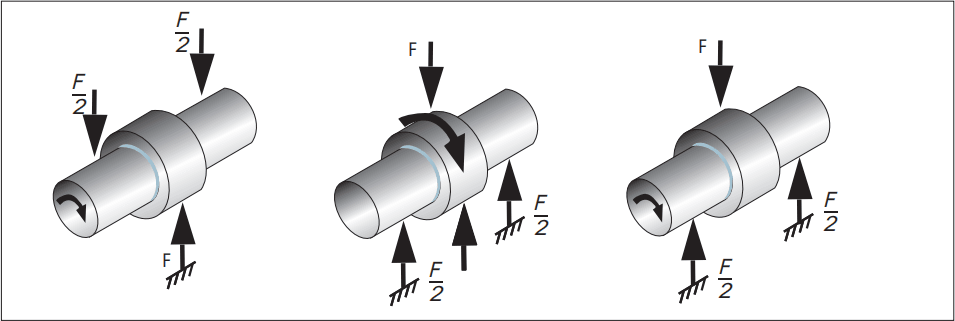
Type of load
Velocity
The main cause of generated heat is the work done at the friction surface of the bearing. It is known from experience that the rise in temperature at the friction surface is affected more by the velocity than by the pressure. With the same PV value, the larger V value is, the high bearing temperature will be. When used in a high velocity operation, it is recommended that the bearings should be designed and used in such a manner that the co-efficient of friction be reduced by positive supply of oil to enhance both cooling and lubricating effectiveness, in order to take advantage of their wear resistance.
Oscillating motion
The oscillating motion is considered to be one of the most severe conditions to bearings zero velocity in each cycle of motion. Oil film is liable to be disrupted, fatigue and wear of material be accelerated and wear particles tend to remain longer. The ball bearing which are designed mainly for rotational motion have a very small contact area causing, extremely high contact stress to develop at their pressure supporting areas. They are, thus, unsuitable for oscillating motion because the contact area of the sleeve bearings are larger than that of the ball bearings, the sleeve bearings are generally considered better for this application. CSB self-lubricating bearings are the most adequate bearings for oscillating motion having a very tough sliding surface which generates little wear particles, and being an oil-containing type which will not cause noise due to disruption of oil film.
Bearing temperature
The life of a bearing is greatly influenced by environment temperature and friction heat that is generated from oscillating and reciprocating motion. For a high temperature application, the PV value of the bearing should be limited to a small value. The heat resistance of plastic bearings is generally inferior to that of metallic bearings. In particular thermoplastic resins are poor resistance to heat. Also the thermal expansion rate of them is relatively high. Consequently, in order to maintain a minimum required clearance, it is important to emphasis on the dimensional control during the designation of bearings made by these materials.
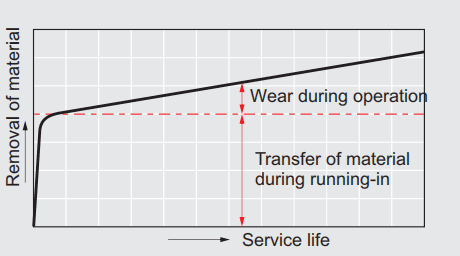
Operation intervals
Operation may either be continuous or intermittent. Intermittent operations can be advantageous for general type bearings because of intervals which allow generated friction heat to cool down. This enables a PV value to remain relatively high. The disadvantage of intermittent operations is that frequent operational interruptions tend to cause inadequate amount. Moreover, resulting in increasing wear occur when restarting. The heavy load imposed in an intermittent operation is liable to cause boundary lubrication condition. A bearing should be selected which safely endures friction and wear in that condition. Oil-containing bearings self-supply lubricant oil to the sliding surface, and exhibit excellent lubricant maintaining capability. CSB650# in particular has a high load carrying capacity and displays excellent performance in intermittent operations with high load because of the tough film of solid lubricants covers the sliding surface.